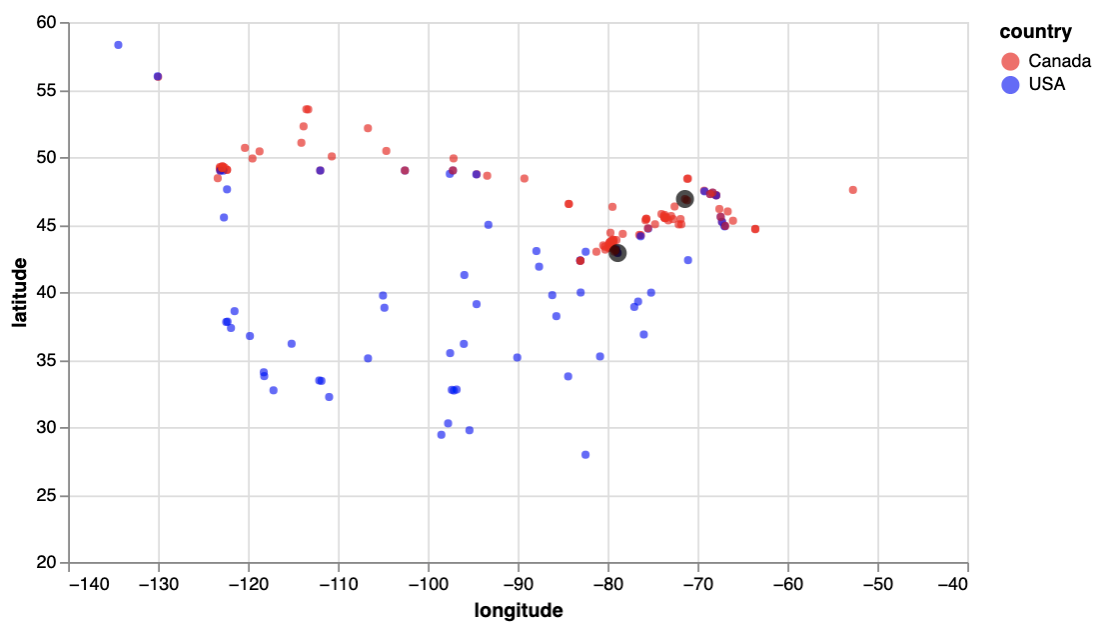
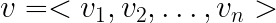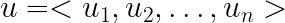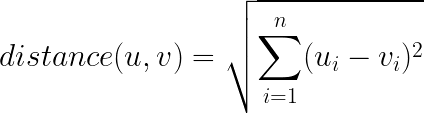cities_df = pd.read_csv("data/canada_usa_cities.csv")
train_df, test_df = train_test_split(cities_df, test_size=0.2, random_state=123)
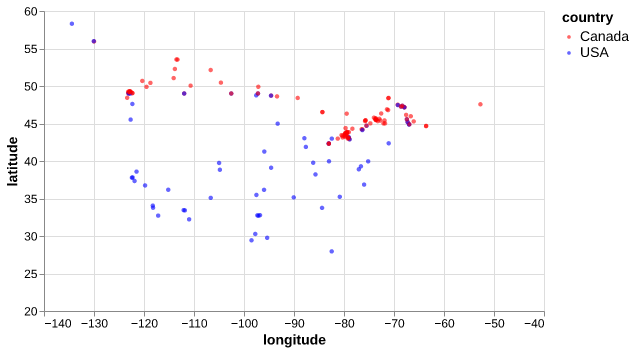
train_df.head()| longitude | latitude | country | |
|---|---|---|---|
| 160 | -76.4813 | 44.2307 | Canada |
| 127 | -81.2496 | 42.9837 | Canada |
| 169 | -66.0580 | 45.2788 | Canada |
| 188 | -73.2533 | 45.3057 | Canada |
| 187 | -67.9245 | 47.1652 | Canada |